(1) Criteria for reference selection
References that satisfied all of the following 3 criteria were included:
- 1) References using Kampo formulations approved for manufacture and sale in Japan
(excluding in-house formulations such as decoctions, because of unknown quality of the medicines used) - 2) Randomized controlled trials (R CTs), quasi-randomized controlled trials (quasi-RCTs), crossover trials, and meta-analyses
(including some with randomization procedure not fully indicated. Crossover trials are regarded as RCT) - 3) References published in or after 1986
Those published in or after 1986 obviously using formulations of 1985 or previous quality, which differs from the current quality levels, were excluded throughout the study period.
(2) Search and screening
Searches were performed using the two databases listed below, with additional reports collected by hand searches. Screening was performed in 2 steps: first, the references that obviously did not satisfy the criteria were excluded by the search staff; then, the remaining references were reviewed to finally select the ones to undergo the process of structured abstract preparation as described below.
1) The Cochrane CENTRAL (C)
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), which is the world’s largest database of RCTs, was used to search for RCTs of Kampo medicines. Cochrane was formerly known as the Cochrane Collaboration, founded in 1992, and the name was changed as of 30 January 2015.
https://www.cochrane.org/news/announcing-cochranes-new-brand-identity
CENTRAL is a database dedicated to RCTs, identified from searches of the PubMed and Embase databases, and from hand searches of journals.
https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central
For this reason, no direct search of PubMed has been conducted in this project since its beginning.
On 1 April 2016, searches were performed by using the following search formula and limited to articles published in and after 1986:;
#1 MeSH descriptor Medicine, East Asian Traditional explode all trees
#2 MeSH descriptor Medicine, Kampo explode all trees
#3 MeSH descriptor Medicine, Chinese Traditional explode all trees
#4 MeSH descriptor Drugs, Chinese Herbal explode all trees
#5 MeSH descriptor Herb-Drug Interactions explode all trees
#6 MeSH descriptor Herbal Medicine explode all trees
#7 MeSH descriptor Plants, Medicinal explode all trees
#8 MeSH descriptor Plant Structures explode all trees
#9 MeSH descriptor Plant Extracts explode all trees
#10 MeSH descriptor Materia Medica explode all trees
#11 MeSH descriptor Phytotherapy explode all trees
#12 (Kampo):ti,ab,kw
#13 (Kanpo):ti,ab,kw
#14 (Japanese):ti,ab,kw
#15 (Oriental):ti,ab,kw
#16 (Traditional):ti,ab,kw
#17 (East Asia):ti,ab,kw
#18 (East-Asia):ti,ab,kw
#19 (Herb*):ti,ab,kw
#20 (Chinese):ti,ab,kw
#21 (#1 OR #2 OR #3 OR #4 OR #5 OR #6 OR #7 OR #8 OR #9 OR #10 OR #11 OR #12 OR #13 OR #14 OR #15 OR #16 OR #17 OR #18 OR #19 OR #20), from 1986 to 2012
#22 (HS-EKAT)
#23 (#21 AND NOT #22)
In October 2011, of the RCT papers on Kampo formulations appearing EKAT 2010 under the “Reference(s)” of structured abstracts, those that had not been previously listed in CENTRAL were so listed and after HS-EKAT tagging, were linked to the EKAT SAs on the JSOM website. The present search excludes 352 papers with “HS-EKAT” in the search formula, so as to exclude those papers related SAs.
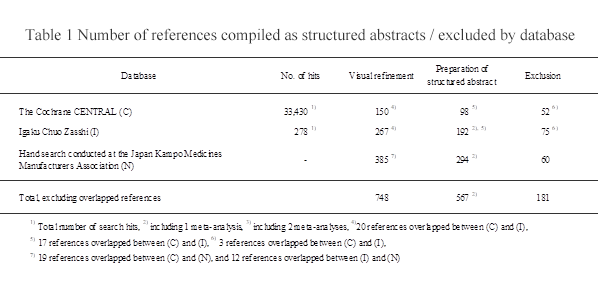
Out of 33,430 search hits, 150 Kampo references were visually confirmed. Among the Kampo references identified by searching the CENTRAL database, 20 references were also found in the Ichushi Web database.
Kampo-related reports accounted for approx. 0.4% of the total hits.
Finally, of the 150 references, 98 satisfying the inclusion criteria were compiled as structured abstracts; the remaining 52 were cited as excluded references along with bibliographic items and the reason for exclusion.
2) Ichushi Web (I)
Ichushi Web, the Japan Medical Abstracts Society’s database available on the Internet, was used to search for RCTs of Kampo medicines on 1 April 2016, using the following search formula:
Search formula:
(漢方薬 [Kampo medicine]/TH or漢方 [Kampo]/AL) and (メタアナリシス [meta-analysis]/RD or ランダム化比較研究 [randomized controlled trial]/RD or 準ランダム化比較研究 [quasi-randomized controlled trial]/RD) and (DT=1986: 2015)
Since the Ichushi Web tags meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, and quasi-randomized controlled trials, the present search targeted references that were tagged (メタアナリシス [meta-analysis]/RD or ランダム化比較研究 [randomized controlled trial]/RD or 準ランダム化比較研究 [quasi-randomized controlled trial]/RD), had “漢方薬 [Kampo medicine]” (漢方薬 [Kampo medicine]/TH) as a keyword (control term), or a title or abstract including the term “Kampo [漢方]” (漢方 [Kampo]/AL), and were published between 1986 and 2015 (DT=1986:2015).
As a result, 278 references were identified (20 of them were also CENTRAL hits). Of these references, 192 satisfying the inclusion criteria were selected and compiled as structured abstracts (191 RCTs and 1 meta-analysis). Of the references compiled as structured abstracts, one included 2 RCTs, for which separate structured abstracts were prepared.
The Ichushi Web assigns the keyword “漢方 [Kampo]” to traditional Chinese medicines and food and Indian medicines as well. These references, in addition to references to randomized studies not evaluating Kampo medicine, non-clinical articles, and citations of existing references, totaled 75 and were not compiled as structured abstracts. They were listed as excluded references along with bibliographic items and the reason for exclusion.
3) Hand searches conducted at the Japan Kampo Medicines Manufacturers Association (N)
Hand searches were conducted at the Japan Kampo Medicines Manufacturers Association (JKMA) on 1 April 2016 to identify articles published in or after 1986 about Kampo or crude drugs collected by member companies of JKMA. The following key terms were used in the search strategy.
Keywords: the search terms are given in their original form (words in parentheses indicate search terms or hits in Roman characters, and the corresponding meanings in English):
- メタアナリシス (meta-anarisisu, meta-analysis); メタ解析(meta-kaiseki, meta-analysis); メタ分析(meta-bunseki, meta-analysis); RCT; ランダム(randamu, random); 無作為, 無作意(musakui, random); 封筒(futo, envelope); 来院順 (raiinjun, order of presentation); 受診順 (jushinjun, order of presentation); 診断順 (shindanjun, order of diagnosis); 割付, 割り付け (;waritsuke, allocation); ブラインド (buraindo, blind); 盲検, 盲験(mouken, blind), 遮蔽, 遮へい, しゃへい (shahei, mask), マスク (masuku, mask); マスキング (masukingu, masking); クロスオーバー (kurosuoba, crossover), 交叉, 交差 (kosa, crossover), 比較臨床 (hikaku rinsho, controlled clinical); random; cross over; meta analysis; envelope
SAs were prepared for 294 hand-searched articles that did not duplicate articles obtained in CENTRAL or Ichushi Web searches. Among the source articles of SAs, three articles respectively contained two RCTs, and thus separate SAs were prepared for each RCT. No SAs were prepared for 60 hand-searched articles that failed to meet the inclusion criteria. For these excluded articles, the bibliographic information and the reasons for exclusion are provided in the list of excluded references.
Overall, from the two databases and hand searches, 748 articles were identified, as shown in Table 1. SAs were prepared for 567 of these articles, and the remaining 181 appear in the excluded references list along with bibliographic information.
(3) Preparation of structured abstracts
The references satisfying the inclusion criteria were compiled as structured abstracts (SA). Studies on SA started in the 1980s. Here, an 8-item structured abstract format of RCTs, as proposed by Altman, et al. and currently used worldwide, was employed.
Altman DG, Gardner MJ. More informative abstracts. Ann Inter Med 1987; 107(5): 790-1.
Aoki T. Kozoka shoroku no kisochisiki (Basic understanding in structured abstracts). In: Tsutani K, Yamazaki S, Sakamaki H (eds). EBM no tameno joho senryaku – ebidensu wo tsukuru, tsutaeru, tsukau – (Information strategies for EBM – generate, transfer and use evidence–). Tokyo: Chugai-igakusha; 2000: 82-93 (in Japanese).
Here, 8 items are referred to as, 1) objectives, 2) design, 3) setting, 4) participants, 5) intervention, 6) main outcome measures, 7) main results, and 8) conclusions.
These 8 items are widely used in medical journals such as JAMA and secondary information journals such as Evidence Based Medicine, ACP Journal Club, as well as in secondary information journals on traditional medicine and complementary and alternative medicine, represented by Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies (FACT). The acupuncture part of the journal is available in Japanese (Tsutani K [supervise-trans]. Hari no ebidensu [Evidence for acupuncture – abstracts of articles on clinical evaluation of acupuncture–]. Yokosuka: Ido-no-Nippon-sha; 2003 [in Japanese]. Thereafter, serialized in the journal “IDO-NO NIPPON [The Japanese Journal of Acupuncture & Manual Therapies]” [in Japanese]).
If one SA has been based on multiple references, all the bibliographic information for references used for the SA appears at the top of the SA, in order of publication, with the principle reference appearing in bold type.
Regarding 5) intervention, since the quality may differ among manufacturers, the brand name indicated in the original article was to be used as a rule. When the brand name was changed after the issue of the article for such reason as a change in manufacturer name, the brand name indicated in the article was used.
In the structured abstracts in the “Evidence Reports of Kampo Treatment”, in addition to the above-mentioned 8 worldwide standard items, the following 4 items are included: 9) from the Kampo medicine perspective; 10) safety assessment in the article; 11) abstractor’s comments; and 12) abstractor and date. These are described below:
9) “From the Kampo medicine perspective” means how the unique diagnosis system of Kampo medicine is used. This is applied to 2 processes: design of a clinical trial and analysis after completion of the study. With RCT, this can be referred to as pre-randomization and post-randomization. In the former process of designing clinical trial design, “sho (証, pattern)” of Kampo medicine is indicated in the entry criteria and exclusion criteria of participants in the protocol in a manner that participating investigators can understand. The latter process involves stratified analysis, in which participants are stratified by “sho” (with sho or without sho), as well as by age and sex, etc. However, the stratified analysis is associated with “inference multiplicity”; that is, repeated testing of many strata produces false positive results, which indicates a difference when actually there is no difference. Among post-hoc approaches are adjustment for covariates.
10) Safety assessment in the article” was incorporated since not only efficacy but also safety should always be considered in Kampo medicine as well. Here, the expression of “safety assessment in the article” was used rather than mere “safety assessment” because “safety assessment” is frequently misunderstood. RCTs usually use efficacy-related endpoints to determine appropriate sample sizes, and are not intended to assess safety. For instance, when no adverse drug reactions occurred among 100 subjects receiving a Kampo medicine, the Kampo medicine is apt to be considered “safe because there are no adverse drug reactions when used in as many as 100 subjects.” Certainly, point estimation yields an incidence of 0%; however, interval estimation yields a 95% confidence interval (CI) for the incidence of 0-3%. Especially when a serious adverse drug reaction may infrequently occur, safety should be judged in consideration of the number of participants in the clinical trial in the article. From this perspective, the expression of “safety assessment in the article” was used.
Reports on Kampo medicines sometime use expressions such as “30 patients received the treatment, and had no adverse reactions”. However, caution is required here in two respects.
First, an adverse drug reaction is different from an adverse event. An adverse event (AE) means “any untoward medical occurrence, whether or not related to the medical product,” and an adverse drug reaction (ADR) means an AE with “causal relationship to the medical product that cannot be ruled out”.
Second, for probabilistic reasons, a confidence interval (CI) is necessary, and usually a 95% CI is used. Its upper and lower limits are referred to as confidence limits. For example, if 10 patients are treated and no adverse events occur, the 95% CI is 0–26%; if 20 patients are treated, the 95% CI is 0–14%; if 50 patients, 0–6%; if 100 patients, 0–3%; and if 500 patients, 0–0.6%. When the sample size is greater than 50, the rule of three can be used to give approximate results. The lower confidence limit is always zero, while the upper confidence limit is [1-0.051/n]. A detailed explanation of the above can be found in the reference cited below.
Tsutani K. Kenkyu dezain no kiso (Research design basics). In: Tsutani K et al. (eds). EBM no tameno joho senryaku – ebidensu wo tsukuru, tsutaeru, tsukau – (Information strategies for EBM – generate, transfer, and use evidence –). Tokyo: Chugai-igakusha; 2000: 26-47. (in Japanese)
The above example assumed no occurrence of adverse events in any patients. Generally, however, when “adverse events occurred in m of n patients”, the 95% CI can be calculated based on binomial distribution using the equation below. This equation, which utilizes normal approximation of binominal distribution, produces larger error with smaller sample size (n < 25).
95% confidence interval for event incidence=p±1.96√(p(1-p) /n), where p=m/n.
Although normal approximation was used for calculating the confidence interval in the above equation, there are other calculation systems readily available on the Internet.
In this evidence report, the description in “safety assessment included in the article” is standardized as follows:
- 1) Without indication
- When safety assessment was not performed or indicated, “none” was indicated.
- 2) With indication
- When safety assessment was performed, even if only slightly, and revealed no adverse drug reactions, that effect was indicated. When adverse drug reactions were specifically indicated, the abstractor in charge indicated this according to the expression used in the reference. When the number of patients with adverse drug reactions was specified in the reference, it was indicated. Note that some indications of adverse drug reactions are not unified.
11) Abstractor’s comments” refers to objective comments on a reference presented as a structured abstract. This helps busy readers not used to critical appraisal correctly and easily judge the value of the article. Abstractors were selected such that the abstractor did not belong to the same group of the authors concerned or have a master-student relationship, in consideration of conflict of interest (COI). How comments should be made was most actively discussed among members of the task force. With the aim of improving and standardizing comments, the 2nd Workshop of the Task Force for Evidence Report “To prepare appropriate comments” was held in conjunction with the Japan Society for Oriental Medicine 58th Annual Meeting held in Hiroshima on 17 Jun. 17, 2007.
12) Abstractor and date” is intended to clarify the responsibility, which also concerns the abovementioned conflict of interest, and to show the temporary relationship between the comments and related studies and in consideration of the possibility of correction at a later date. When a structured abstract was revised, the date of revision was added.
Structured abstract preparation tasks were assigned to Task Force members in consideration of their specialties. However, since the specialties of members did not cover the whole field, some abstracts were prepared by non-specialized members.
Bibliographic items were indicated in the Vancouver style as a rule, with some modifications, including that the number of authors listed shall be up to 3 and that the name of a journal shall not be abbreviated.
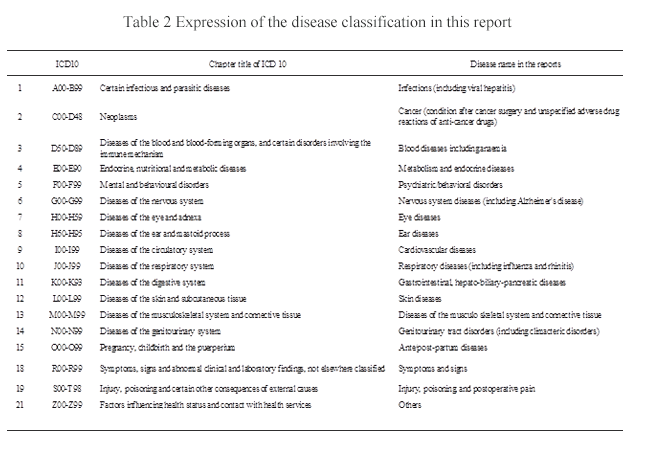
Structured abstracts were arranged in the order of ICD10 (Version 2003) code of diseases. Those with the same code were arranged by date of publication of the main reference evaluated. When more than one ICD code was possible, the one seeming to be generally more understandable was selected. Similarly, excluded references were arranged in the order of ICD10 code. The names of Kampo formulae, etc. that could not be written in Chinese characters for daily use in Japan were written in Katakana. The names of ICD code diseases differ from general names and were therefore read as shown in Table 2 to indicate them in this report.
In preparing structured abstracts, to maintain the quality, a Structured Abstract Preparation Manual was prepared, distributed to Task Force members, and updated as appropriate.
